Part 1: PROJECT 2025 IS US (U.S.)
To where the seed was planted, and how far our fascist trees branches go
And now, where were we? Oh yeah, Planting the seed from which PROJECT 2025 grew from..
Various events in U.S. history that could be characterized as tyrannical or fascist, and how these events may have inspired similar actions or movements elsewhere.
THE SEEDLING FOR PROJECT 2025

Establishment of the Colonies
Enslavement and Genocide of Native Americans (1600s-1700s)
- Actions: European colonists, including those in what would become the United States, engaged in the forced removal, enslavement, and genocide of Native American populations. This included massacres, forced relocations, and the spread of diseases.
- Inspiration: This set a precedent for colonial and imperial practices worldwide, inspiring other European powers to engage in similar actions in Africa, Asia, and South America.
- Sources:
- Churchill, W. (1997). A Little Matter of Genocide: Holocaust and Denial in the Americas 1492 to the Present. City Lights Books.
- Stannard, D. E. (1992). American Holocaust: The Conquest of the New World. Oxford University Press.
Revolutionary War and Early Republic
The Alien and Sedition Acts (1798)
- Actions: Enacted under President John Adams, these laws allowed the government to deport foreigners and made it harder for new immigrants to vote. They also criminalized making false statements that were critical of the federal government.
- Inspiration: These acts reflected similar laws in European monarchies aimed at suppressing dissent and maintaining control over populations.
- Sources:
- Smith, J. M. (2010). Freedom's Fetters: The Alien and Sedition Laws and American Civil Liberties. Cornell University Press.
- Miller, J. C. (1951). Crisis in Freedom: The Alien and Sedition Acts. Little, Brown and Company.
19th Century
Trail of Tears (1830s)
- Actions: Under President Andrew Jackson, the Indian Removal Act led to the forced relocation of thousands of Native Americans, resulting in the deaths of thousands from exposure, disease, and starvation.
- Inspiration: This forced migration echoed the colonial practices of other nations and foreshadowed similar forced relocations, such as those seen in Stalin's Soviet Union
- Sources:
- Ehle, J. (1988). Trail of Tears: The Rise and Fall of the Cherokee Nation. Doubleday.
- Perdue, T., & Green, M. D. (2007). The Cherokee Nation and the Trail of Tears. Penguin Books.
The Fugitive Slave Act (1850)
- Actions: This law mandated that escaped slaves found in free states be returned to their enslavers in the South. It imposed heavy penalties on those who helped runaway slaves.
- Inspiration: Similar laws were enacted in other slave-holding societies, and it echoed the strict control measures used by totalitarian regimes to maintain control over populations.
- Sources:
- Finkelman, P. (2011). Slavery and the Founders: Race and Liberty in the Age of Jefferson. M.E. Sharpe.
- Vorenberg, M. (2001). Final Freedom: The Civil War, the Abolition of Slavery, and the Thirteenth Amendment. Cambridge University Press.
Civil War and Reconstruction
Suspension of Habeas Corpus (1861)
- Actions: President Abraham Lincoln suspended the right of habeas corpus during the Civil War, allowing for the arrest and detention of suspected Confederate sympathizers without trial.
- Inspiration: This action was similar to measures taken by various European monarchs and later dictators, such as the Nazis, to suppress dissent and maintain control during times of crisis.
- Sources:
- Neely, M. E. Jr. (1991). The Fate of Liberty: Abraham Lincoln and Civil Liberties. Oxford University Press.
- White, J. W. (2011). Abraham Lincoln and Treason in the Civil War: The Trials of John Merryman. LSU Press.
Late 19th and Early 20th Century
Jim Crow Laws (late 1800s-1960s)
- Actions: These laws enforced racial segregation and disenfranchised African Americans in the Southern United States. They were backed by widespread violence and intimidation, including lynchings.
- Inspiration: The system of racial segregation and disenfranchisement inspired similar practices in other countries, such as apartheid in South Africa.
- Sources:
- Woodward, C. V. (2001). The Strange Career of Jim Crow. Oxford University Press.
- Litwack, L. F. (1998). Trouble in Mind: Black Southerners in the Age of Jim Crow. Vintage.
The Palmer Raids (1919-1920)
- Actions: Led by Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer, these were a series of raids conducted to arrest and deport suspected radical leftists and anarchists.
- Inspiration: These raids were part of a broader Red Scare and inspired similar anti-communist purges in Europe, such as the actions taken by fascist regimes in Italy and Germany.
- Sources:
- Murray, R. K. (1964). Red Scare: A Study in National Hysteria, 1919-1920. University of Minnesota Press.
- Coben, S. (1991). A. Mitchell Palmer: Politician. Columbia University Press.
World War II Era
Internment of Japanese Americans (1942-1945)
- Actions: During World War II, the U.S. government forcibly relocated and interned around 120,000 Japanese Americans, citing national security concerns.
- Inspiration: This action mirrored the treatment of ethnic minorities in other wartime states, such as Nazi Germany's treatment of Jews and other minority groups.
- Sources:
- Robinson, G. (2001). By Order of the President: FDR and the Internment of Japanese Americans. Harvard University Press.
- Daniels, R. (2005). Prisoners Without Trial: Japanese Americans in World War II. Hill and Wang.
Cold War Era
McCarthyism (1950s)
- Actions: Led by Senator Joseph McCarthy, this was a campaign against alleged communists in the U.S. government and other institutions, characterized by aggressive investigations and questioning.
- Inspiration: McCarthyism inspired similar anti-communist measures worldwide, including in Europe and Latin America, and echoed the tactics of authoritarian regimes to suppress dissent.
- Sources:
- Schrecker, E. (1998). Many Are the Crimes: McCarthyism in America. Little, Brown and Company.
- Fried, A. (1990). McCarthyism: The Great American Red Scare: A Documentary History. Oxford University Press.
Late 20th and Early 21st Century
War on Drugs (1980s-present)
- Actions: Initiated under President Ronald Reagan, the War on Drugs led to mass incarceration, especially of African Americans and Latinos, often for minor offenses. It also involved militarized police tactics and mandatory minimum sentencing.
- Inspiration: The U.S. approach influenced other countries, particularly in Latin America, to adopt harsh anti-drug measures and increase militarization of their law enforcement.
- Sources:
- Alexander, M. (2010). The New Jim Crow: Mass Incarceration in the Age of Colorblindness. The New Press.
- Baum, D. (1997). Smoke and Mirrors: The War on Drugs and the Politics of Failure. Little, Brown and Company.
Post-9/11 Measures (2001-present)
- Actions: Following the September 11 attacks, the U.S. government implemented the USA PATRIOT Act, which expanded surveillance capabilities, allowed indefinite detention of immigrants, and increased government powers to combat terrorism.
- Inspiration: These measures inspired similar anti-terrorism laws and practices worldwide, many of which were used to justify suppressing political dissent and violating human rights.
- Sources:
- Cole, D., & Dempsey, J. X. (2006). Terrorism and the Constitution: Sacrificing Civil Liberties in the Name of National Security. The New Press.
- Greenwald, G. (2006). How Would a Patriot Act? Defending American Values from a President Run Amok. Working Assets Publishing.
Meandering Muse is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.

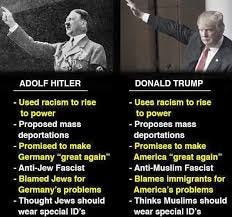

Recent Trends
Immigration Policies and Detention Camps (2017-2021)
- Actions: Under President Donald Trump, policies like family separations at the border and the use of detention camps for migrants were implemented.
- Inspiration: These actions drew comparisons to internment practices and were cited by other countries with harsh immigration policies.
- Sources:
- Lind, D. (2019). The U.S. Immigration System May Have Reached Peak Cruelty. Vox. Retrieved from https://www.vox.com
- Warren, R. (2019). Family Separation: A Timeline of the Trump Administration’s Zero Tolerance Policy. The American Immigration Council.
Protests and Government Response (2020-present)
- Actions: The government’s response to protests, particularly those related to the Black Lives Matter movement, included the use of militarized police, tear gas, and mass arrests.
- Inspiration: This inspired similar crackdowns on protests in other countries and reflected tactics used by authoritarian regimes to suppress civil unrest.
- Sources:
- Buchanan, L., Bui, Q., & Patel, J. K. (2020). Black Lives Matter May Be the Largest Movement in U.S. History. The New York Times. Retrieved from https://www.nytimes.com
- Simon, D. (2020). Trump Administration Deploys Federal Agents to Portland, What We Know. NPR. Retrieved from https://www.npr.org
There is another step or two before we get to the image of the end.. I want to empower everyone to fight against fascism through changing hearts before desiring to burn it all down. Too many—usually unconsidered —vulnerable communities pay the price. As the research is intense, I hope to have the next step done in less than two weeks.
As always, I appreciate and WELCOME comments/ questions, feedback/suggestions of topics.
~~🍀Ginge 🍀
Meandering Muse is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.






